O'Donnell et al.
Dec 18, 2024
This perspective article discusses recent advancements and challenges in applying machine learning (ML) to analyze adaptive immune receptor repertoires (AIRRs), particularly focusing on B cell receptors (BCRs) and T cell receptors (TCRs).
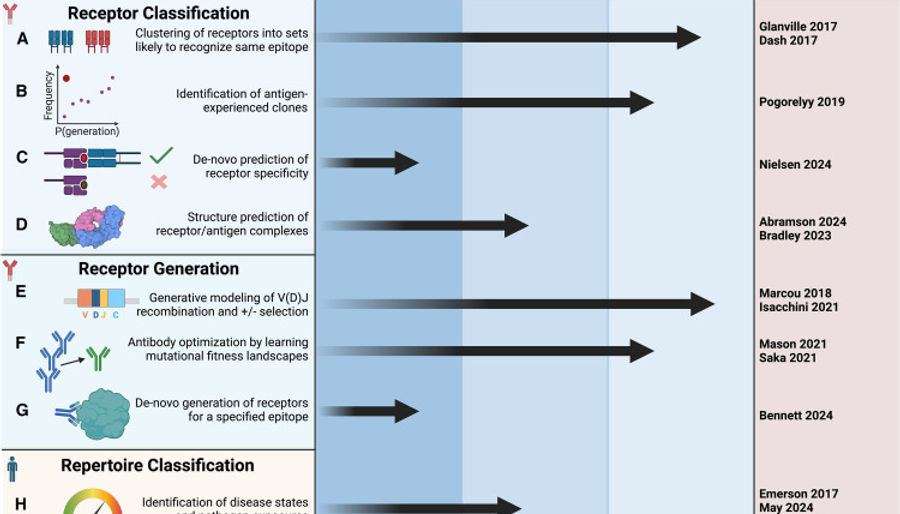
O'Donnell et al. discusses recent advancements and challenges in applying machine learning (ML) to analyze adaptive immune receptor repertoires (AIRRs), particularly focusing on B cell receptors (BCRs) and T cell receptors (TCRs). The primary goal is to unlock the vast biological information encoded in immune receptor sequences to improve diagnostics, therapeutics, and vaccines. The key areas of ML application include:
Receptor Classification: Predicting antigen specificity, which remains a core unsolved challenge due to the vast diversity and complexity of immune receptors.
Receptor Generation: Using ML models to generate receptor sequences with desired properties, including those relevant for therapeutic use.
Repertoire Classification: Classifying immune states or diseases based on repertoire data, although this is hindered by data scarcity and the complexity of immune responses.
This paper emphasizes the need for improved software benchmarking, large-scale data generation, and coordinated research to overcome these challenges. It also highlights the importance of collaborative efforts to create standardized, AI-ready datasets that can enable better performance of ML models and enhance the interpretability of AIRR data. To advance the field, there is a call for more efficient and reproducible methods, the development of specific models for diverse immune states, and the integration of structure-based predictions for receptor-antigen interactions.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405471224003429